Novel Computing for Artificial Multimodal Perception Algorithms
Artificial perception plays a key role in the development of Intelligent Systems and Robotics. As a spin-off of computer vision and pattern recognition, there has been a focus on artificial multimodal perception for cognitive systems. The sensation-cognition-action loop needs to deal with uncertainty, and probabilistic approaches provide a robust solution, so novel solutions in Bayesian Computation have been pursued.
A key contribution in artificial multimodal perception for cognitive systems was on the actual way Bayesian computations are done. We are developing artificial perception algorithms, including integrated mult-isensory computational models. These include probabilistic approaches towards a new generation of algorithms to deal with uncertainty, ambiguities and conflicts inherent to the perceptual process that promote intelligent and adaptive decisions on actions in the physical world.
The main goals are:
- Integrated multisensory computational models and systems;
- Intelligent and adaptive cognitive decision and action/actuation processes;
- Computational models and devices to deal with uncertainty, ambiguities and conflicts inherent to the perceptual process.
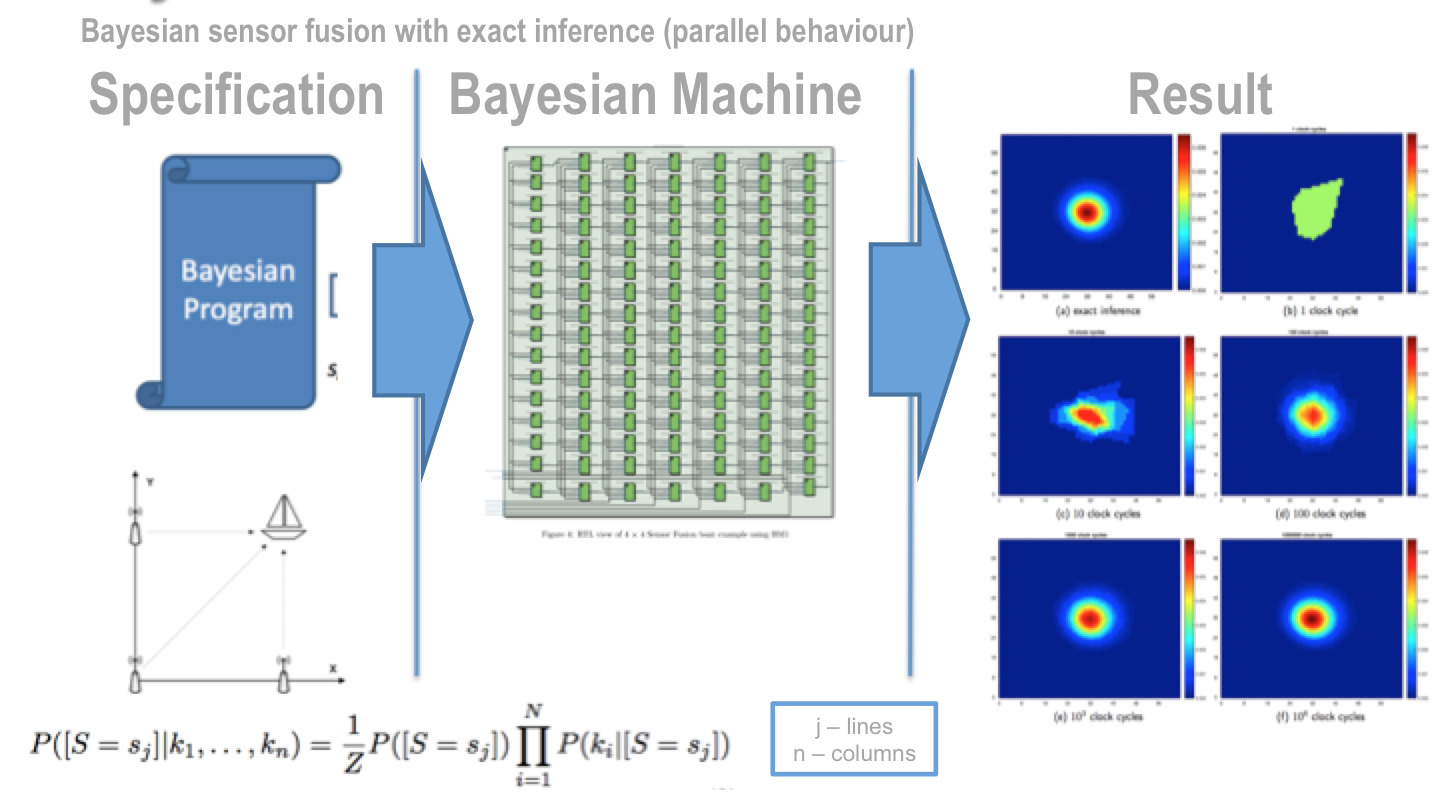
In the scope of an European FET project, we developed Bayesian probabilistic processors that capture the results from neuromorphic computing onto robotics. The goal is to replace the digital approaches by systems directly operating on probability distributions. This has enabled us to continue to develop Bayesian hierarchical models that can be implemented in real-time.
This was done concurrently with the development of artificial perception algorithms with integrated multisensory computational models mimicking cognitive systems. These include probabilistic approaches towards a new generation of algorithms to deal with uncertainty, ambiguities and conflicts inherent to the perceptual process that promote intelligent and adaptive decisions on actions in the physical world.
Key related publications:
J. Lobo, J. F. Ferreira, Unconventional computing for Bayesian inference, International Journal of Approximate Reasoning, Volume 88, 2017, Pages 306-308 DOI: 10.1016/j.ijar.2017.06.004
Ferreira, J. F. ; Dias, Probabilistic Approaches for Robotic Perception". Springer Tracts in Advanced Robotics (STAR) 91, 2014, http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-02006-8, ISBN 978-3-319-02006-8
J. S. Friedman, J. Droulez, P. Bessière, J. Lobo, D. Querlioz, Approximation enhancement for stochastic Bayesian inference, International Journal of Approximate Reasoning, Volume 85, June 2017, Pages 139-158, ISSN 0888-613X DOI: 10.1016/j.ijar.2017.03.007
P. Lanillos Pradas, J. F. Ferreira, J. Dias, A Bayesian Hierarchy for Robust Gaze Estimation in Human-Robot Interaction, Int. J. of Approximate. Reasoning, 87, 1-22, 2017 DOI: 10.1016/j.ijar.2017.04.007